Vehicle Inspection Checklist
A vehicle inspection checklist is a structured method used by fleet teams to verify vehicle safety, compliance, and operational readiness before and after use, as well as during scheduled maintenance cycles. Consistent inspections reduce breakdown risk, support regulatory compliance, and create traceable maintenance records for operational decision-making.

Defect Workflow Summary
| Step | Responsible Role | Required Action | Evidence / Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| Defect Identified | Driver / Technician | Note issue and severity | Inspection form entry |
| Documentation | Driver / Supervisor | Add photos / notes | Timestamped record |
| Triage & Approval | Fleet Manager | Assign priority and downtime | Work order created |
| Repair Execution | Technician / Vendor | Complete corrective work | Service invoice / checklist |
| Verification & Closeout | Supervisor | Confirm repair and release | Signed approval record |
Driver-Only Inspections vs Layered Inspections

Driver-Only Inspections
- Faster completion time before dispatch
- Limited mechanical depth
- Higher risk of overlooked defects
- Dependent on driver training consistency

Driver + Technician Layered Inspections
- Broader mechanical coverage
- Increased defect detection accuracy
- Stronger accountability chain
- Better audit and compliance reliability
Inspection Program Basics
An effective inspection program defines who inspects, what is inspected, and how often inspections occur. Without formal structure, fleets often experience inconsistent reporting and incomplete documentation.
- Establish written inspection policies by vehicle class
- Define inspection frequency (pre-trip, post-trip, periodic)
- Assign accountability to specific roles
- Standardize checklist formats across locations
- Review inspection outcomes monthly
Outcome
- Reduced variability in inspection quality
- Clear ownership of vehicle safety checks
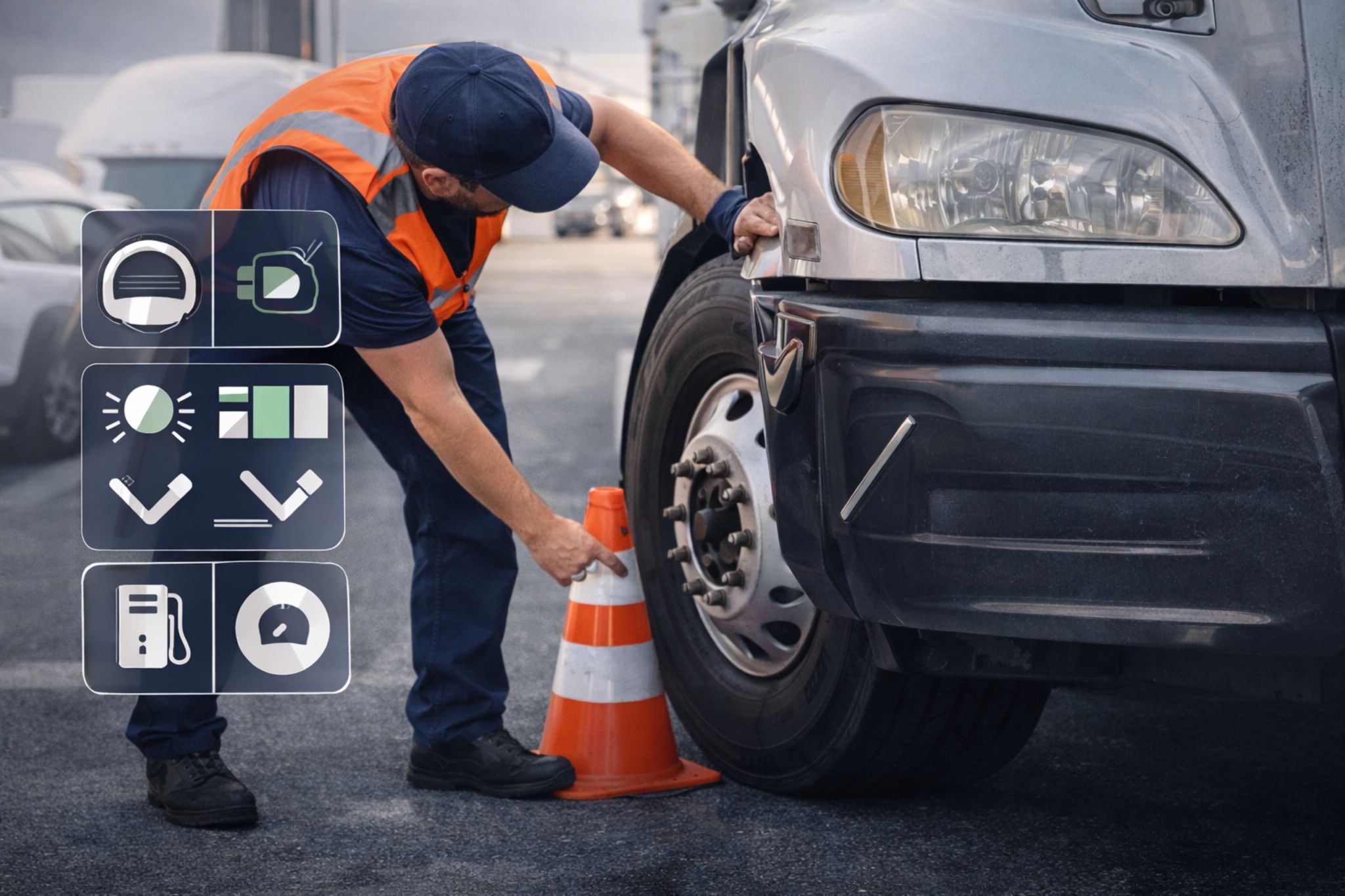


Pre-Trip and Post-Trip Driver Inspections
Driver inspections are the first operational control layer. These checks focus on visible safety and functionality indicators before a vehicle enters service and immediately after use.
- Tires, tread depth, and visible damage
- Lights, signals, and reflectors
- Mirrors, windshield, and wipers
- Fluid leaks or unusual odors
- Dashboard warning indicators
Outcome
- Early detection of high-risk defects
- Immediate removal of unsafe vehicles from rotation
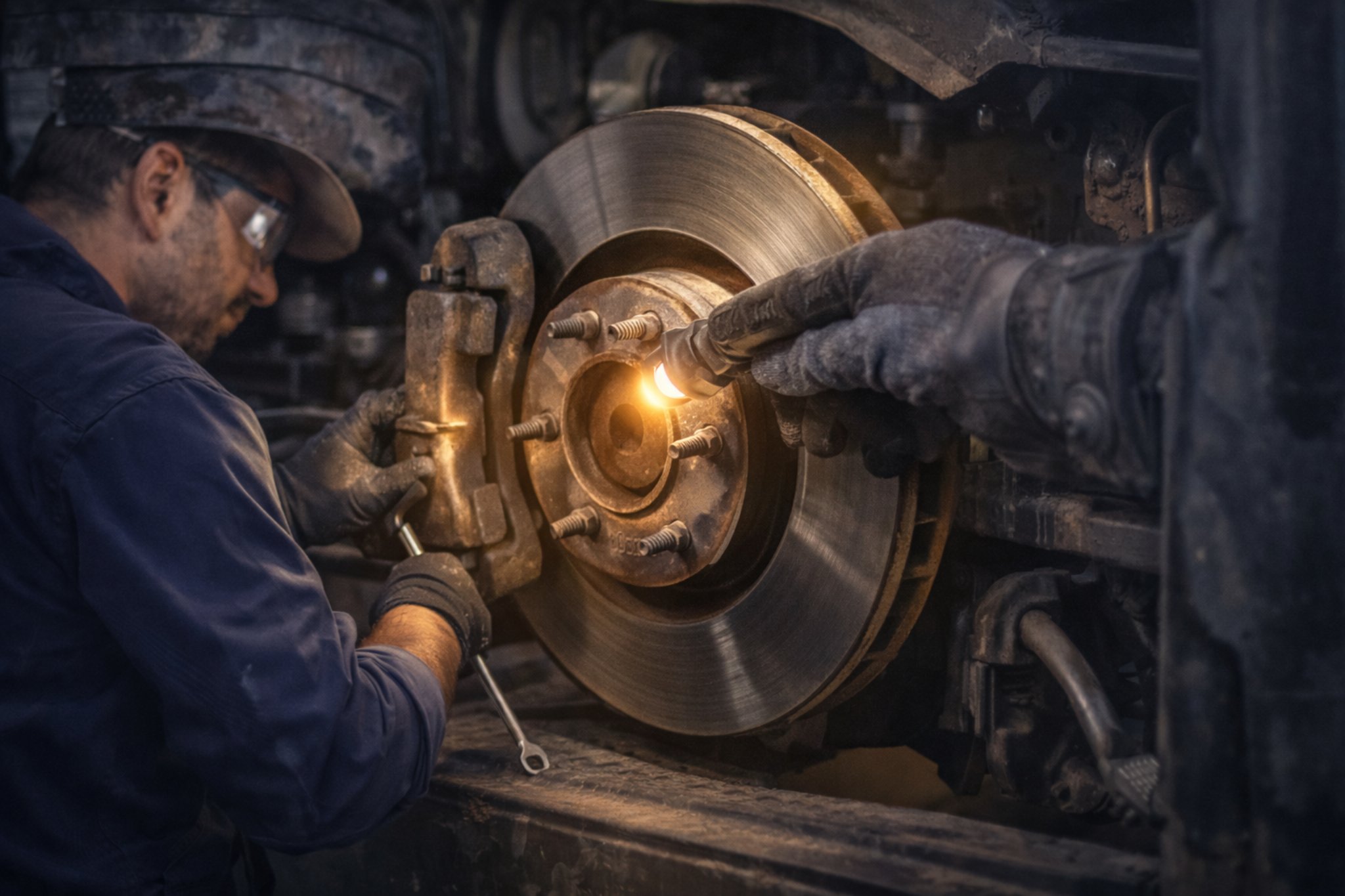
Scheduled Preventive Inspections
Scheduled inspections complement driver checks by focusing on mechanical and system-level components that require tools or technical expertise. These inspections are typically aligned with mileage or time intervals and often reference established preventive maintenance frameworks such as the preventative maintenance guide for fleet operations.
- Brake systems and suspension components
- Steering linkage and alignment indicators
- Engine diagnostics and emissions systems
- Battery health and electrical systems
- Undercarriage corrosion or structural wear
Outcome
- Lower probability of unexpected failures
- Improved asset lifespan predictability


Defect Reporting, Repair Verification, and Closeout
Inspection value is lost if defects are not tracked through to resolution. A defined reporting and verification process ensures that identified issues are corrected and documented.
- Capture defect severity and location details
- Assign repair responsibility with deadlines
- Link inspection records to work orders
- Require supervisory verification before return to service
- Archive completed repair evidence
Outcome
- Transparent maintenance history
- Reduced recurrence of unresolved issues
Records, Audit Readiness, and Continuous Improvement
Inspection documentation supports both compliance audits and operational analytics. Maintaining centralized, searchable records enables faster audit preparation and informed maintenance planning. Reference materials such as a fleet maintenance audit checklist can help standardize documentation expectations.
- Store inspection forms with timestamps
- Retain photos, invoices, and technician notes
- Track recurring defects by vehicle ID
- Review inspection failure trends quarterly
- Update checklist items based on incident findings
Outcome
- Faster audit preparation
- Data-driven inspection improvements

Final Takeaways
A vehicle inspection checklist is not only a safety measure but a structured operational control that supports maintenance planning and compliance assurance.
- Define inspection frequency and role ownership clearly.
- Separate driver checks from technical inspections.
- Ensure every defect follows a documented workflow.
- Maintain centralized records for audits and analysis.
- Continuously refine checklist items based on data.
AUTOsist Fleet Management Resources

Preventative Maintenance Guide for Fleet Operations

Fleet Maintenance Audit Checklist
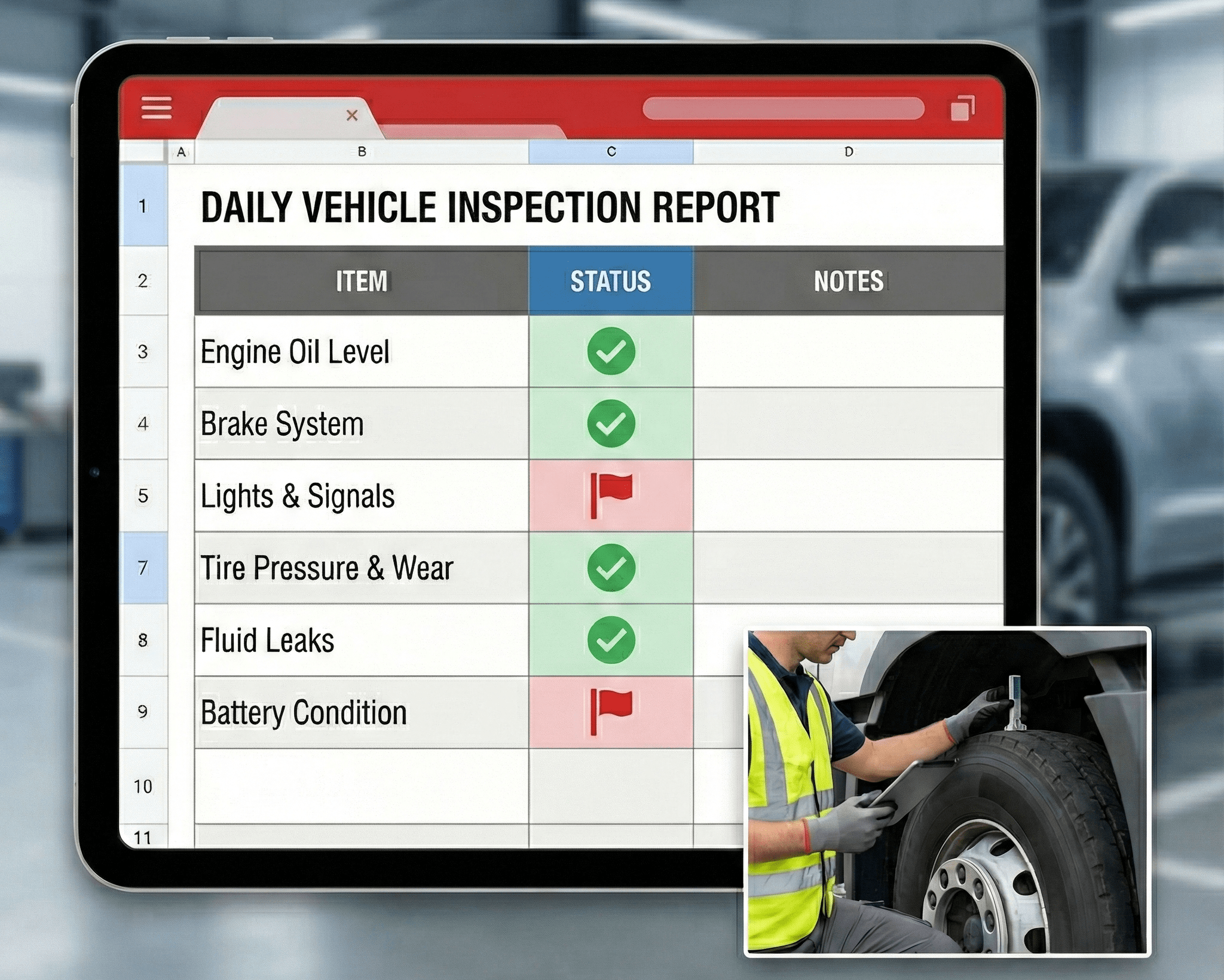
Daily DVIR Vehicle Inspection Checklist PDF
Fleet Maintenance Software