Fleet Maintenance SOP Guide
A Fleet Maintenance Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) is a structured document that defines how vehicle maintenance activities are planned, executed, recorded, and reviewed. It ensures consistency, accountability, compliance readiness, and predictable operational uptime across all fleet assets.

SOP Component Overview
| Component | Purpose | Owner | Update Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scope Definition | Define vehicles and maintenance types covered | Fleet Manager | Annual |
| Roles & Responsibilities | Clarify task ownership and approvals | Operations Lead | Annual |
| Maintenance Procedures | Standardize preventive and corrective actions | Maintenance Supervisor | Semi-Annual |
| Documentation Standards | Ensure audit-ready records | Compliance Officer | Quarterly |
| Review & Improvement | Track KPIs and revise SOP | Fleet Manager | Quarterly |
SOP Governance Model Comparison

Centralized SOP Governance
- Single policy owner with enterprise-wide standards
- Uniform maintenance intervals and approval chains
- Easier compliance audits and reporting consistency
- Stronger change control and version management

Decentralized SOP Governance
- Local teams adapt procedures to vehicle usage patterns
- Faster response to site-specific operational needs
- Higher flexibility for vendor and parts sourcing
- Increased risk of inconsistent documentation standards
Defining Scope and Objectives of the SOP
A clear scope prevents ambiguity and ensures the SOP aligns with operational and compliance requirements. The document should explicitly state what is covered and why the procedure exists.
- Vehicle categories included (light-duty, heavy-duty, equipment)
- Maintenance types covered (preventive, corrective, emergency)
- Regulatory boundaries and jurisdictional considerations
- Operational goals such as uptime targets and cost control
- Alignment with organizational safety policies
Outcome Gist
- Clear inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Reduced interpretation gaps across teams


Roles, Responsibilities, and Approval Structure
An SOP must define who performs each action and who authorizes it. This avoids delays, duplicated work, and unapproved maintenance spending.
- Fleet manager ownership of policy and KPI oversight
- Technician responsibilities for inspections and repairs
- Driver responsibilities for daily checks and defect reporting
- Vendor and contractor authorization levels
- Escalation paths for emergency or high-cost repairs
Outcome Gist
- Faster decision cycles
- Transparent accountability trails
Preventive, Corrective, and Emergency Procedures
Standardized procedures ensure that maintenance actions are repeatable and measurable. Preventive work reduces unexpected downtime, while corrective and emergency processes control risk when failures occur.
- Preventive schedules based on mileage, engine hours, or OEM guidance
- Corrective repair workflows triggered by inspection findings
- Emergency roadside response steps and contact protocols
- Parts approval thresholds and cost authorization limits
- Post-service verification and return-to-service checks
Outcome Gist
- Predictable service intervals
- Reduced unplanned vehicle outages


Documentation, Recordkeeping, and Audit Readiness
Accurate records are central to compliance, warranty validation, and lifecycle cost analysis. Documentation standards should be uniform across all locations and vehicle types.
- Digital work orders with timestamps and technician notes
- Inspection logs and defect resolution tracking
- Service history retention periods and archiving rules
- Fuel, mileage, and parts usage documentation
- Audit checklists and retrieval procedures
Outcome Gist
- Faster audit preparation
- Reliable lifecycle cost visibility
SOP Review, Metrics, and Continuous Improvement
An SOP is not static. Regular performance reviews and revision cycles maintain relevance as fleet size, regulations, and technology evolve.
- KPI tracking (uptime %, cost per mile, mean time between failures)
- Quarterly or semi-annual SOP revision schedules
- Feedback loops from technicians and drivers
- Training refreshers and onboarding alignment
- Vendor performance reviews and contract updates
Outcome Gist
- Data-driven refinements
- Sustained operational consistency

Final Takeaways
A Fleet Maintenance SOP provides structure that translates directly into reliability, compliance readiness, and financial predictability.
- Define scope and ownership clearly before implementation.
- Standardize preventive, corrective, and emergency workflows.
- Maintain uniform documentation and retention practices.
- Track KPIs and revise procedures on a fixed schedule.
- Align SOP governance with organizational size and complexity.
AUTOsist Fleet Management Resources

Fleet Manager Guide

Fleet Compliance Guide
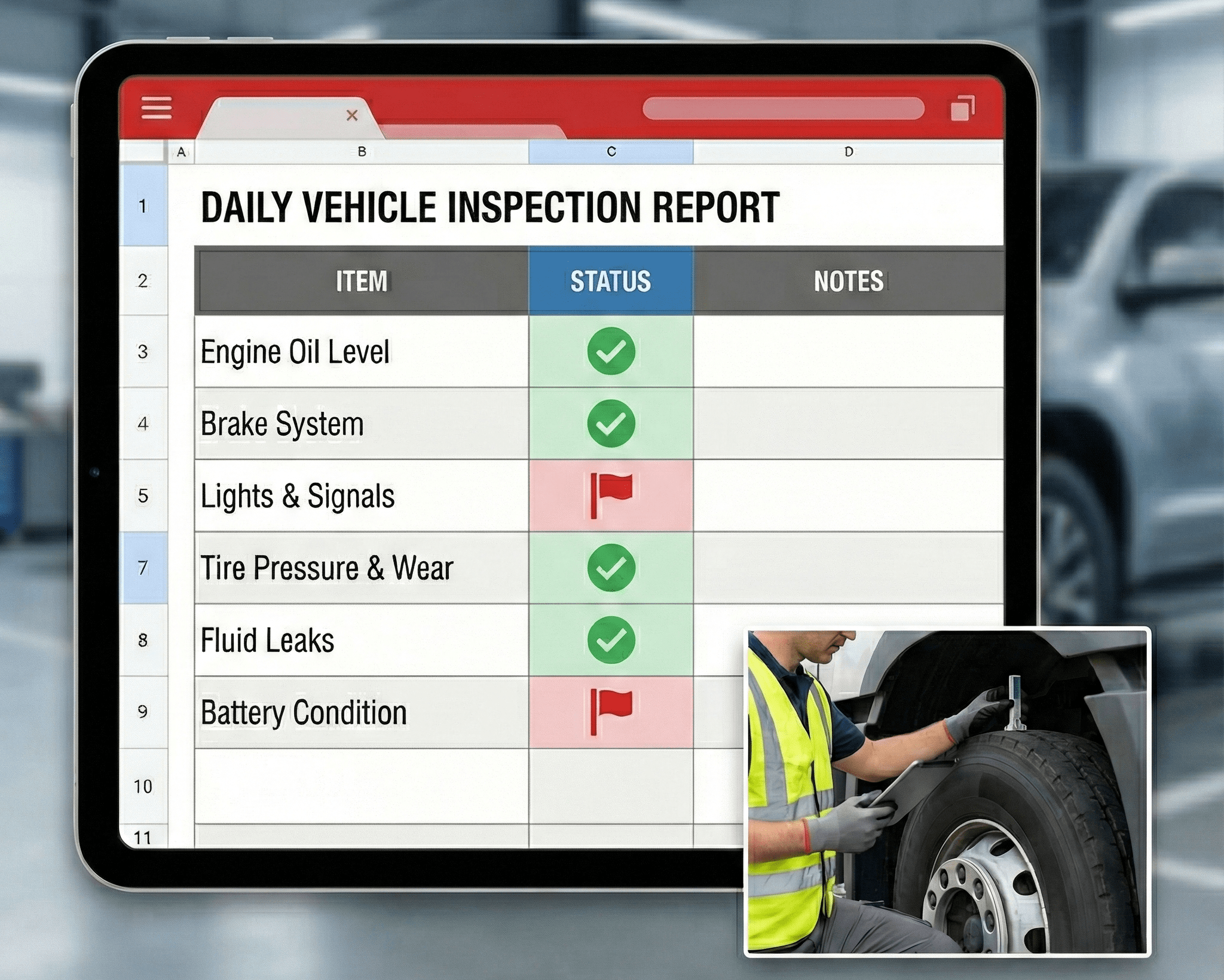
Fleet Maintenance Log Excel Template
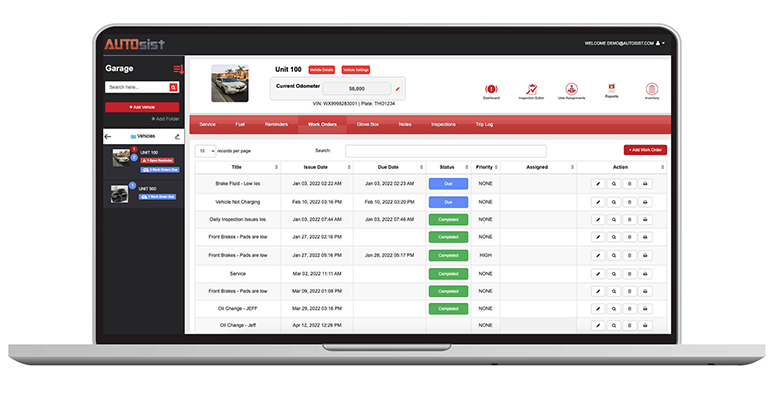
Fleet Maintenance Work Order Software