Fleet Compliance Guide
Fleet compliance is the ongoing process of meeting regulatory, safety, and operational requirements that govern how fleet vehicles, drivers, and maintenance activities are managed. For fleet managers, compliance is not a one-time task but a continuous operational responsibility that directly affects safety outcomes, audit readiness, and business risk.

Fleet Compliance Categories and Required Records
| Compliance Area | Required Records | Responsible Role | Review Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Driver qualifications | Licenses, medical certificates | Fleet manager | Annual |
| Vehicle safety | Inspection and defect reports | Maintenance team | Daily |
| Preventive maintenance | Service logs, repair records | Maintenance supervisor | Ongoing |
| Hours of service | Driver logs, duty status | Operations | Daily |
| Incident management | Accident and incident reports | Safety manager | Per event |
Reactive Compliance Response vs Proactive Compliance Management

Reactive Compliance Response
- Action occurs after violations or incidents
- Higher likelihood of fines and penalties
- Unplanned audits and inspections
- Limited long-term risk mitigation

Proactive Compliance Management
- Continuous monitoring and scheduled reviews
- Lower exposure to enforcement actions
- Predictable audits with prepared documentation
- Stronger long-term compliance control
Understanding Fleet Compliance Requirements
Fleet compliance requirements are shaped by regulatory bodies, vehicle classifications, and how vehicles are used in daily operations. Fleets must clearly understand which rules apply to avoid gaps that lead to violations.
- Identify federal, state, and local regulations affecting operations
- Determine compliance obligations by vehicle type and usage
- Assign ownership for each compliance responsibility
- Monitor regulatory updates and enforcement trends
- Align internal policies with external requirements
Outcome
- Clear compliance scope
- Reduced regulatory uncertainty


Core Compliance Areas Fleets Must Manage
Compliance oversight typically focuses on a defined set of operational areas that regulators evaluate during inspections and audits. Weakness in any area can affect the entire fleet’s compliance standing.
- Driver qualification and credential verification
- Vehicle inspection and defect resolution processes
- Preventive maintenance scheduling and documentation
- Hours-of-service and mileage tracking
- Incident reporting and corrective action tracking
Outcome
- Consistent compliance coverage
- Lower inspection and audit risk
Documentation, Recordkeeping, and Audit Readiness
Documentation quality is one of the most common factors cited in compliance violations. Fleets must maintain accurate, accessible records to demonstrate compliance during audits and inspections. Guidance from resources such as How to Track Fleet Maintenance (Step-by-Step) helps clarify how maintenance records support broader compliance requirements.
- Maintain standardized records across compliance categories
- Follow minimum retention requirements for each record type
- Update records immediately after triggering events
- Store documentation in a centralized, searchable system
- Conduct periodic internal record reviews
Outcome
- Faster audit response
- Fewer documentation-related violations


Operational Risks of Non-Compliance
Non-compliance introduces risks that extend beyond regulatory penalties. These risks often affect daily operations, cost control, and fleet reputation. Related guidance in the Fleet Manager Guide outlines how compliance failures can cascade into broader operational issues.
- Fines, penalties, and out-of-service orders
- Increased insurance premiums and scrutiny
- Vehicle downtime and missed service commitments
- Legal exposure following accidents
- Damage to customer and regulator trust
Outcome
- Clear visibility into compliance-related risk
- Stronger justification for structured compliance processes
Final Takeaways
Fleet compliance is an operational discipline that requires clear ownership, consistent documentation, and proactive oversight. Fleets that treat compliance as a structured process are better positioned to manage risk and maintain continuity.
- Compliance spans drivers, vehicles, maintenance, and documentation
- Record accuracy directly affects audit outcomes
- Proactive compliance reduces cost and disruption
- Clear accountability improves consistency
- Centralized records simplify oversight
AUTOsist Fleet Management Resources

How to Track Fleet Maintenance (Step-by-Step)

Fleet Manager Guide
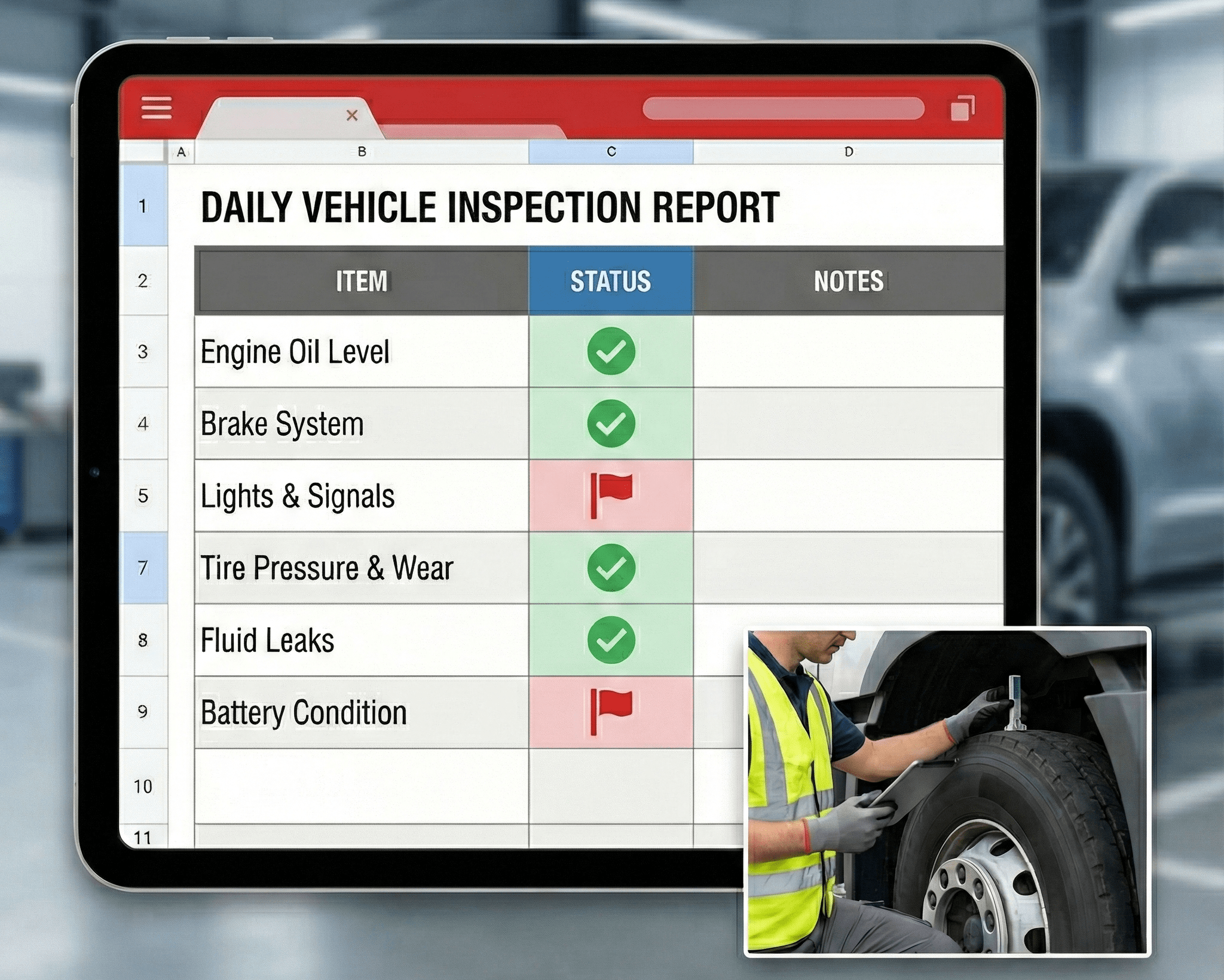
Daily DVIR Vehicle Inspection Checklist PDF
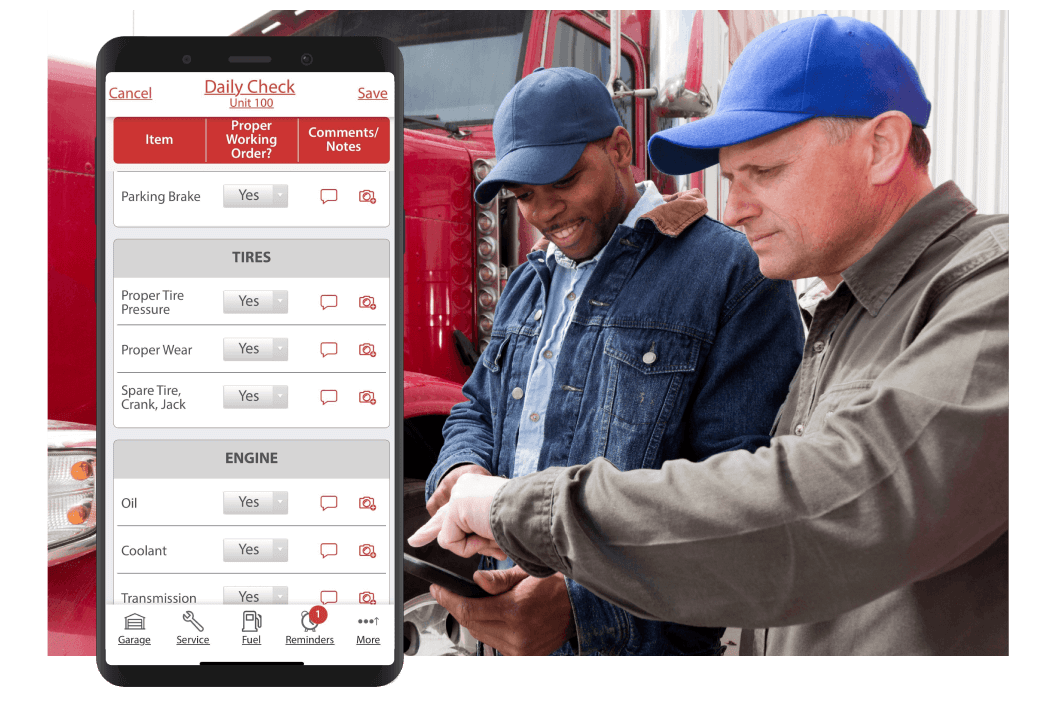
Digital Vehicle Inspection App